Your Ultimate Guide to Capital Gains Tax Exemptions in India!
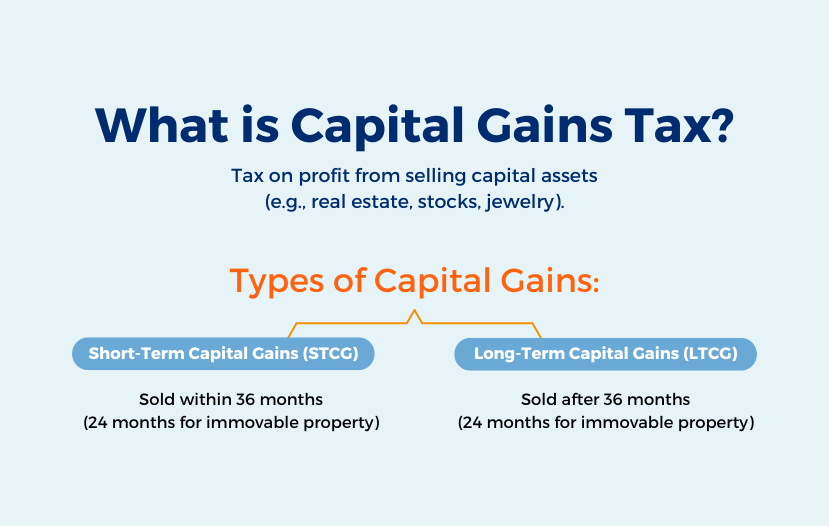
When you sell a capital asset—such as real estate, stocks, or jewellery—and make a profit, you are liable to pay tax on that profit. This tax is known as capital gains tax. In India, capital gains are categorized into two types based on the period of holding: short-term capital gains (STCG) and long-term capital gains (LTCG).
Short-Term Capital Gains (STCG): If you sell an asset within 36 months (24 months for immovable property such as land or building) of acquiring it, the profit earned is classified as short-term capital gains.
Long-Term Capital Gains (LTCG): If you sell an asset after 36 months (24 months for immovable property) of acquiring it, the profit earned is classified as long-term capital gains.
Tax Rates on Capital Gains
STCG: Taxed as per the individual's income tax slab rates.
LTCG: Taxed at 20% after indexation benefits for most assets.
For equity shares and equity-oriented mutual funds, LTCG exceeding ₹1 lakh in a financial year is taxed at 10% without indexation.
Saving Capital Gains Taxes
The Income Tax Act provides several provisions under which individuals can save on capital gains taxes by investing the profits in specific ways.
The government allows you to reduce or defer the taxes you owe on these gains by reinvesting the money in specific ways. This is known as a capital gains exemption.
Let's look at some of these options in detail:
Section 54: Exemption on Sale of Residential Property
Applicability: Individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs).
Conditions:
Asset involved: Residential property.
Type of gains exempt: Long-term capital gains.
Time limit for investing: Purchase another residential property within 1 year before or 2 years after the sale, or construct within 3 years.
Amount of exemption: Lower of the capital gains or the cost of the new residential property.
Example:
Mr. A sells his house in June 2024 for ₹80 lakhs, making a long-term capital gain of ₹20 lakhs. He buys another house for ₹25 lakhs within two years.
Exemption: Entire ₹20 lakhs capital gain is exempt under Section 54.
Section 54B: Exemption on Sale of Agricultural Land
Applicability: Individuals and HUFs.
Conditions:
Asset involved: Agricultural land (urban or rural).
Type of gains exempt: Short-term or long-term capital gains.
Time limit for investing: Purchase another agricultural land within 2 years.
Amount of exemption: Lower of the capital gains or the cost of the new agricultural land.
Example:
Mrs. B sells her agricultural land for ₹50 lakhs, making a capital gain of ₹10 lakhs. She buys new agricultural land for ₹15 lakhs within two years.
Exemption: Entire ₹10 lakhs capital gain is exempt under Section 54B.
Section 54D: Exemption on Compulsory Acquisition of Land and Building used in Industrial undertaking
Applicability: Individuals, HUFs, and companies.
Conditions:
Asset involved: Land and buildings used for industrial purposes.
Type of gains exempt: Short-term or long-term capital gains.
Time limit for investing: Purchase or construct new land or building within 3 years.
Amount of exemption: Lower of the capital gains or the cost of the new land/building.
Example:
Company C’s industrial land is compulsorily acquired by the government, resulting in a capital gain of ₹30 lakhs.The company buys new industrial land for ₹35 lakhs within three years.
Exemption: Entire ₹30 lakhs capital gain is exempt under Section 54D.
Section 54EC: Exemption on Sale of Long-Term Capital Assets
Applicability: Individuals, HUFs, and others.
Conditions:
Asset involved: Any long-term capital asset (e.g., land, building).
Type of gains exempt: Long-term capital gains.
Time limit for investing: Investment in specified bonds (e.g., NHAI, REC) within 6 months.
Amount of exemption: Up to ₹50 lakhs.
Example:
Mr. D sells his commercial property and earns a long-term capital gain of ₹40 lakhs.He invests ₹40 lakhs in NHAI bonds within six months.
Exemption: Entire ₹40 lakhs capital gain is exempt under Section 54EC.
Section 54EE: Exemption on Investment in Specified Funds
Applicability: Individuals, HUFs, and others.
Conditions:
Asset involved: Any long-term capital asset (e.g., land, building).
Type of gains exempt: Long-term capital gains.
Time limit for investing: Investment in units of specified funds within 6 months.
Amount of exemption: Up to ₹50 lakhs.
Example:
Ms. E sells her property, earning a long-term capital gain of ₹25 lakhs.She invests ₹25 lakhs in the notified units of specified funds within six months.
Exemption: Entire ₹25 lakhs capital gain is exempt under Section 54EE.
Section 54F: Exemption on Sale of Any Long-Term Capital Assets (Other Than a House)
Applicability: Individuals and HUFs.
Conditions:
Asset involved: Any long-term capital asset (e.g., shares, bonds).
Type of gains exempt: Long-term capital gains.
Time limit for investing: Purchase within 1 year before or 2 years after the sale, or construct within 3 years.
Amount of exemption: If entire sale proceeds are invested, the entire capital gain is exempt. If part of the sale proceeds is invested, the exemption is proportionate.
Example:
Mr. F sells his shares, earning a long-term capital gain of ₹10 lakhs and total sale proceeds of ₹30 lakhs.He invests the entire ₹30 lakhs in a residential house within two years.
Exemption: Entire ₹10 lakhs capital gain is exempt under Section 54F.
Conclusion:
Navigating the complexities of capital gains tax can seem daunting, but with the right knowledge and strategic planning, you can significantly reduce your tax burden. By leveraging the exemptions available under Sections 54, 54B, 54D, 54EC, 54EE, and 54F, you can maximize your savings and reinvest your gains wisely. If you're looking to optimize your tax strategy and ensure compliance with the latest tax laws, consult with our tax experts today. Don't leave your tax savings to chance—take control of your financial future now!
Stay tuned for more tax tips and strategies. Happy investing and saving!

